Scaling WhatsApp Message Broadcasting: How We Successfully Sent 50,000 Messages Using the WhatsApp API
Written on November 17, 2024
Views : Loading...

Introduction
Broadcasting large volumes of messages on platforms like WhatsApp can be a daunting task, especially when dealing with scalability and reliability. Recently, I embarked on a project to broadcast 50,000 WhatsApp messages using the WhatsApp API. This blog details the step-by-step process, the challenges encountered, and the solutions implemented to achieve this feat efficiently using Next.js, Vercel, and AWS Lambda functions.
The Challenge
The primary objective was to allow users to select a message template, upload a CSV file containing variables and phone numbers, and broadcast personalized messages to all recipients. However, several challenges needed to be addressed:
- Handling Large CSV Files: Processing a CSV file with 50,000 entries in a single go could overwhelm the server, especially on platforms like Vercel, which have execution time limits.
- API Rate Limits: Sending messages serially at approximately 2 seconds per API call would take around 27 hours, which is impractical.
- Scalability: Ensuring the system could handle high concurrency and large-scale processing without failures.
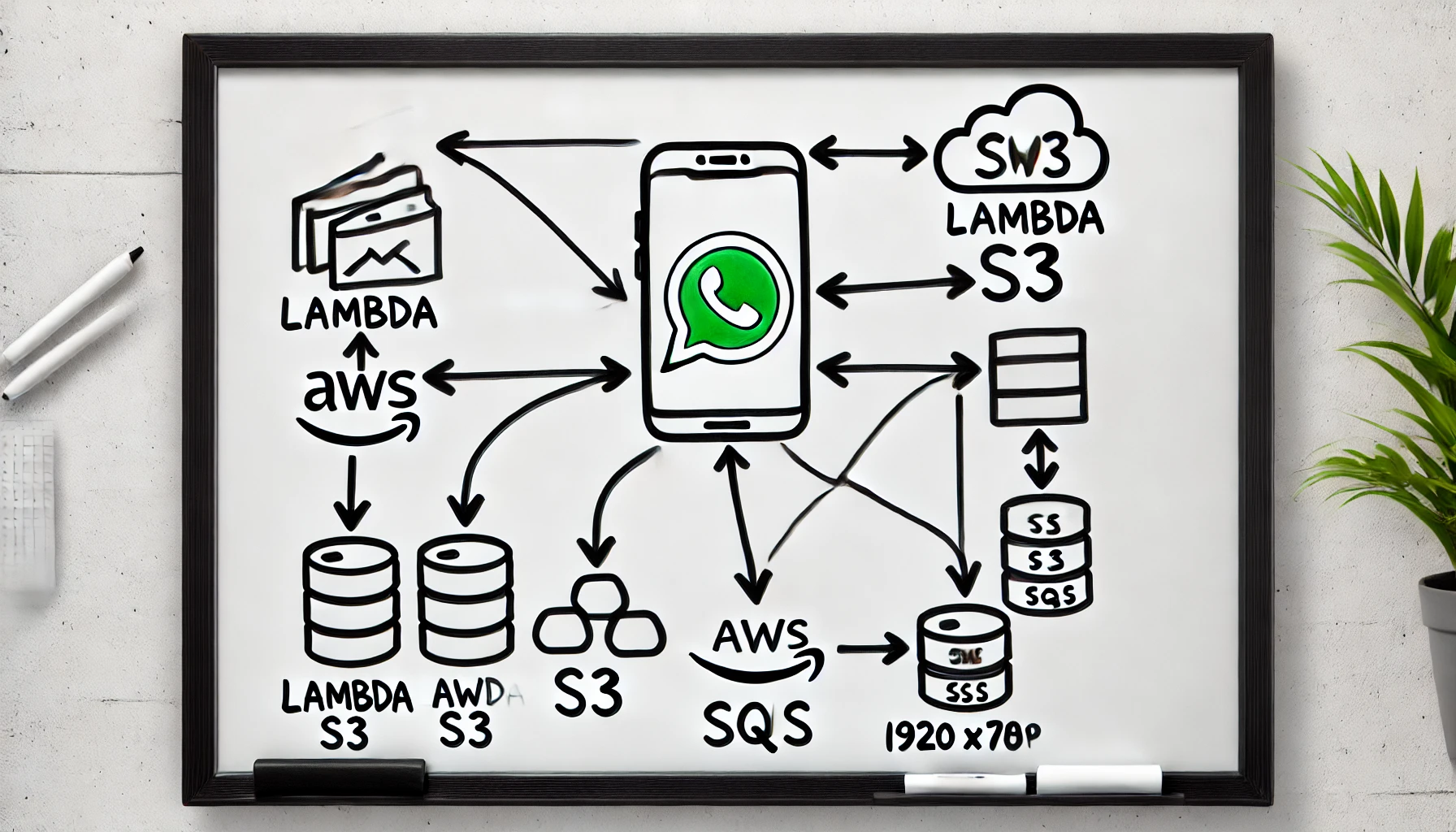
The Solution Architecture
To overcome these challenges, I designed a serverless architecture using AWS services that could efficiently handle the load. Here's an overview of the solution:
-
Frontend (Next.js on Vercel):
- Users select a message template.
- Users upload a CSV file containing variables and phone numbers.
-
AWS S3:
- The CSV file is uploaded to S3 using a pre-signed URL.
-
AWS Lambda Functions:
- First Lambda: Processes the CSV file, converts each row into a JSON payload, and enqueues messages into AWS SQS.
- Second Lambda: Triggers from SQS, batches messages, and sends them via the WhatsApp API.
-
AWS SQS:
- Acts as a queue to manage message payloads and ensure reliable processing.
Step-by-Step Implementation
1. Setting Up the Frontend with Next.js
The frontend allows users to select a message template and upload their CSV file. To handle large file uploads efficiently, a pre-signed URL is generated for direct upload to S3.
// components/UploadForm.jsx
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function UploadForm() {
const [file, setFile] = useState(null);
const [template, setTemplate] = useState('');
const handleSubmit = async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
// Get pre-signed URL from your backend
const res = await fetch('/api/get-presigned-url');
const { url } = await res.json();
// Upload file to S3
await fetch(url, {
method: 'PUT',
body: file,
});
// Notify backend to process the file
await fetch('/api/process-csv', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({ s3Key: 'uploaded-file.csv', template }),
});
alert('Messages are being processed!');
};
return (
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<label>
Select Template:
<select value={template} onChange={(e) => setTemplate(e.target.value)}>
<option value="template1">Template 1</option>
<option value="template2">Template 2</option>
{/* Add more templates as needed */}
</select>
</label>
<br />
<label>
Upload CSV:
<input type="file" accept=".csv" onChange={(e) => setFile(e.target.files[0])} required />
</label>
<br />
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
);
}
2. Handling Large CSV Processing with AWS Lambda
Given that Vercel isn't suitable for processing 50,000 messages in one go, AWS Lambda functions were employed to handle the heavy lifting.
a. Uploading CSV to S3
Users upload the CSV file directly to S3 using a pre-signed URL, ensuring secure and efficient file transfers without overloading the server.
// pages/api/get-presigned-url.js
import AWS from 'aws-sdk';
const s3 = new AWS.S3({
region: 'your-region',
accessKeyId: process.env.AWS_ACCESS_KEY,
secretAccessKey: process.env.AWS_SECRET_KEY,
});
export default async function handler(req, res) {
const params = {
Bucket: 'your-bucket-name',
Key: `uploads/${Date.now()}-${req.body.filename}`,
Expires: 60, // URL expiry time in seconds
ContentType: 'text/csv',
};
const url = s3.getSignedUrl('putObject', params);
res.status(200).json({ url });
}
b. Processing the CSV and Enqueuing Messages
Once the CSV is uploaded, the first Lambda function downloads it from S3, parses each row into a JSON payload, and enqueues messages into SQS in batches of 10.
// lambda/ProcessCSV.js
const AWS = require('aws-sdk');
const csv = require('csv-parser');
const s3 = new AWS.S3();
const sqs = new AWS.SQS();
const P_LIMIT = require('p-limit');
const limit = P_LIMIT(10); // Limit to 10 concurrent SQS sends
exports.handler = async (event) => {
const { s3Key } = JSON.parse(event.body);
const params = { Bucket: 'your-bucket-name', Key: s3Key };
const stream = s3.getObject(params).createReadStream();
const messages = [];
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
stream
.pipe(csv())
.on('data', (row) => {
messages.push({
Id: row.phoneNumber,
MessageBody: JSON.stringify({
phoneNumber: row.phoneNumber,
variables: row.variables, // Adjust based on your CSV structure
}),
});
})
.on('end', async () => {
try {
const batches = [];
while (messages.length) {
batches.push(messages.splice(0, 10));
}
await Promise.all(
batches.map((batch) =>
limit(() =>
sqs.sendMessageBatch({
QueueUrl: 'your-sqs-queue-url',
Entries: batch,
}).promise()
)
)
);
resolve({ statusCode: 200, body: 'Messages enqueued successfully!' });
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
})
.on('error', reject);
});
};
3. Sending Messages via WhatsApp API with the Second Lambda
The second Lambda function is triggered by SQS messages. It batches up to 1,000 messages and sends them through the WhatsApp API using Meta's endpoints.
// lambda/SendWhatsAppMessages.js
const AWS = require('aws-sdk');
const axios = require('axios');
const sqs = new AWS.SQS();
exports.handler = async (event) => {
const messages = event.Records.map((record) => JSON.parse(record.body));
// Batch messages into groups of 1000
const batches = [];
while (messages.length) {
batches.push(messages.splice(0, 1000));
}
await Promise.all(
batches.map(async (batch) => {
const payload = {
messaging_product: "whatsapp",
to: batch.map(msg => msg.phoneNumber),
type: "template",
template: {
name: "your_template_name",
language: { code: "en_US" },
components: [
{
type: "body",
parameters: batch.map(msg => ({ type: "text", text: msg.variables.someVariable })),
},
],
},
};
await axios.post('https://graph.facebook.com/v13.0/your_phone_number_id/messages', payload, {
headers: {
'Authorization': `Bearer your_access_token`,
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
});
})
);
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'Messages sent successfully!' };
};
4. Leveraging AWS SQS for Reliable Messaging
AWS SQS ensures that messages are reliably queued and processed. By decoupling the message processing from the frontend, the system can handle high volumes without overloading any single component.
5. Optimizing Performance and Scalability
- Batch Processing: By sending messages in batches of 10 to SQS and processing 1,000 messages per Lambda invocation, we significantly reduce the number of API calls and enhance throughput.
- Concurrency Control: Using
p-limitensures that we don't exceed the SQS rate limits and maintain efficient processing. - Serverless Architecture: AWS Lambda scales automatically based on the load, ensuring that the system can handle spikes without manual intervention.
Conclusion
Broadcasting 50,000 WhatsApp messages efficiently required a robust, scalable, and reliable architecture. By leveraging Next.js for the frontend, AWS S3 for file storage, Lambda functions for processing, and SQS for message queuing, we successfully scaled our messaging system to handle large volumes seamlessly.
This approach not only ensures scalability but also maintains high performance and reliability, making it a suitable solution for large-scale messaging needs.
Further Reading
If you found this guide helpful, feel free to share it with others
Share this blog
Related Posts
18-05-2025
Learn how to build a robust, serverless application on AWS to perform calculations like $f(x) = x^2 ...

09-02-2025
In this comprehensive blog, discover how to build a production-like AWS environment with a private E...
09-12-2024
This blog is dedicated to simplifying complex mathematical and computational concepts into understan...
01-12-2024
Static Range Sum queries using various Algorithms
30-11-2024
An in-depth exploration of JavaScript iteration methods and best practices in asynchronous programmi...
26-11-2024
An in-depth exploration of an efficient algorithm to compute the sum of Euler's Totient Function up ...
25-11-2024
In the realm of graph theory, understanding the connectivity of a network is crucial for numerous ap...
24-11-2024
Dive deep into the Z Algorithm, a fundamental technique in string processing. This blog elucidates t...

21-11-2024
A comprehensive guide to understanding derangements using the inclusion and exclusion principle.
